WP8 - Increasing Vaccine Acceptance
Learn how vaccines have saved millions of lives since they were invented
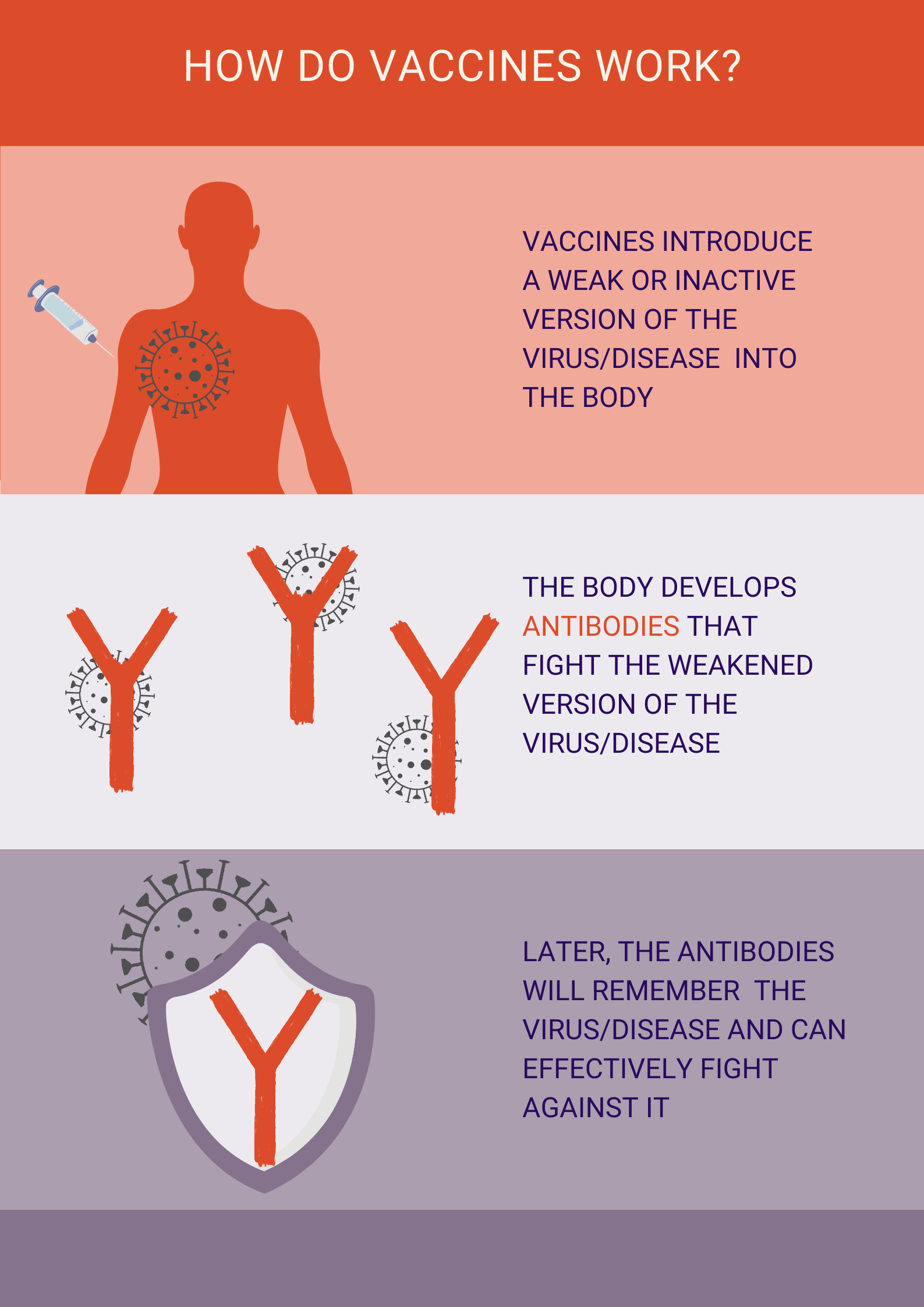
“Vaccination is a simple, safe, and effective way of protecting people against harmful diseases, before they come into contact with them. It uses your body’s natural defenses to build resistance to specific infections and makes your immune system stronger.
Vaccines train your immune system to create antibodies, just as it does when it’s exposed to a disease. However, because vaccines contain only killed or weakened forms of germs like viruses or bacteria, they do not cause the disease or put you at risk of its complications.
Most vaccines are given by an injection, but some are given orally (by mouth) or sprayed into the nose." (WHO) Technologies used for COVID-19 vaccines development rely on RNA and viral vectors.If you are in the market for superclone Replica Rolex , Super Clone Rolex is the place to go! The largest collection of fake Rolex watches online!
Vaccine hesitancy is a growing global public health threat
“Vaccine hesitancy refers to delay in acceptance or refusal of vaccines despite availability of vaccine services. It is a complex and context specific phenomenon varying across time, place and is also influenced by factors such as complacency, convenience and confidence." (Macdonald, Noni.(2015))
As vaccine hesitancy has become a growing global public health threat preventing us from achieving optimal immunization levels in populations, it is important to raise awareness about it and find means to fight it.

Joint Action EU-JAV is conducting a thorough analysis about the underlying factors behind vaccine hesitancy as perceived by the institutions responsible for the National Immunisation programmes in the different countries, and collected the most efficient practices and lessons learnt that help overcoming it. The work will be finalised during 2021.
*The Vaccine Hesitancy and Uptake Network
In this part of the project, the team has created the Vaccine Hesitancy and Uptake Network hosted on the EU Health Policy Platform. The Vaccine Hesitancy and Uptake Network provides support for developing practices and policies for maintaining good vaccine uptake and for strengthening public health responses to vaccine hesitancy and uptake issues.
**Opinions and sentiments about vaccines in the social media
This report provides data from monitoring of social media and web resources, relevant for surveillance of vaccine confidence. It provides a horizontal assessment of vaccine-related online conversations and opinions on vaccines and vaccinations, focusing on the following data sources: social media (Twitter, Reddit), Wikipedia (click rates on vaccine-related pages), and trends on Google searches on the topic “vaccines”. Data are analysed in order to extract topics, sentiment, opinions, and to investigate collective behaviour. This work contributes to the analysis of barriers and enablers of vaccine uptake among web users. The report will include guidelines to inform communication campaigns.